What is Knee Osteoarthritis?
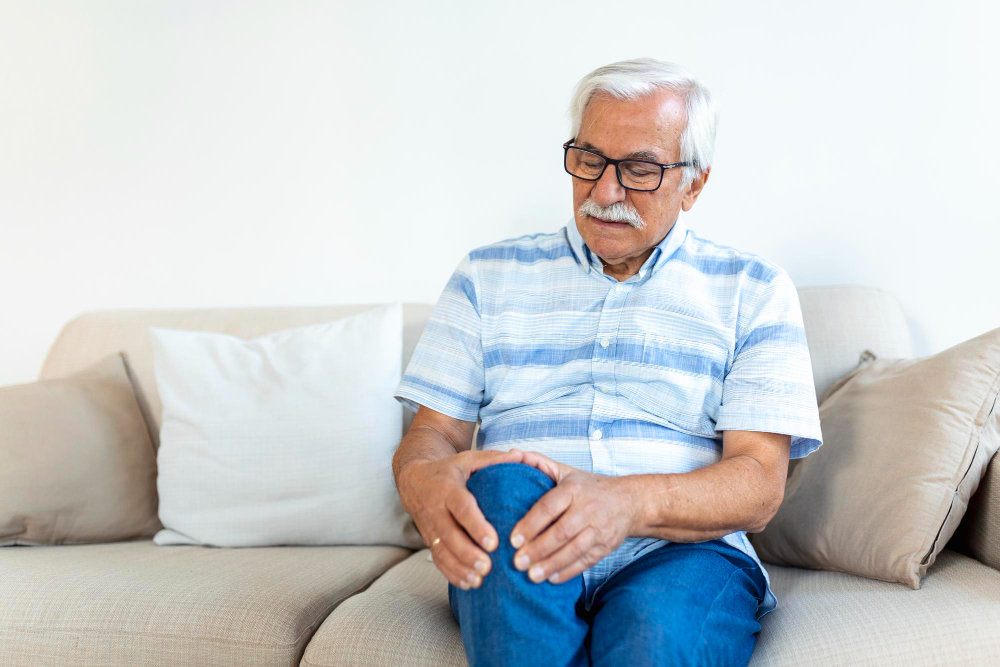
Knee osteoarthritis is a common joint problem. It happens when the cartilage in your knee wears down over time. Because of this, the bones in your knee may rub together. This can cause pain, swelling, and stiffness. Many people over age 50 develop knee osteoarthritis. However, it can affect younger adults too. According to the CDC, millions of people in the United States live with this condition. Early care can help manage knee pain and improve movement.
Common Symptoms of Knee Osteoarthritis
Many people notice symptoms slowly. Sometimes, symptoms get worse after activity. Here are common signs:
Because symptoms can change over time, it is important to track them. This helps your doctor find the best knee pain treatment for you.
Main Causes and Risk Factors
Knee osteoarthritis develops for several reasons. Some causes and risk factors include:
Although you cannot change some risk factors, you can manage others. For example, keeping a healthy weight helps lower your risk.
Diagnosis Methods
Doctors use several methods to diagnose knee osteoarthritis. First, they ask about your symptoms and medical history. Next, they examine your knee for swelling, pain, or movement problems. Sometimes, doctors order tests to confirm the diagnosis. These may include:
Early diagnosis helps you start managing knee arthritis sooner. This can slow down joint damage and improve your quality of life.
Treatment Options for Knee Osteoarthritis
There are many ways to treat knee osteoarthritis. Your doctor will suggest a plan based on your symptoms and needs. Treatment options include:
Medical Treatments
Lifestyle Changes
Physical Therapy
Surgical Options
Because each person is different, your doctor will help you choose the best treatment. Managing knee arthritis often involves a mix of these options.
Prevention Tips and Lifestyle Guidance
While you cannot always prevent knee osteoarthritis, you can lower your risk. Try these tips:
In addition, eating a balanced diet helps keep your joints healthy. Staying active also supports overall well-being.
When to See a Doctor
If you have knee pain that does not improve, see a doctor. You should also seek help if you notice:
Early care can prevent further joint damage and help you find the right treatment sooner.
Consult Dr. Sudeep for personalised advice and expert care on knee osteoarthritis.